
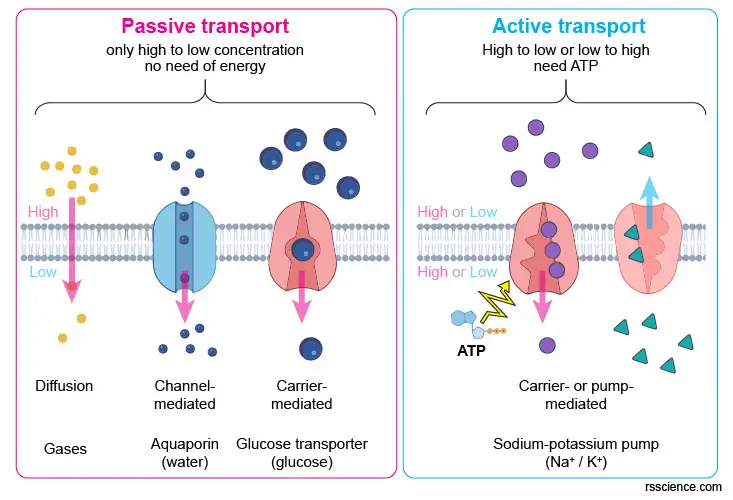
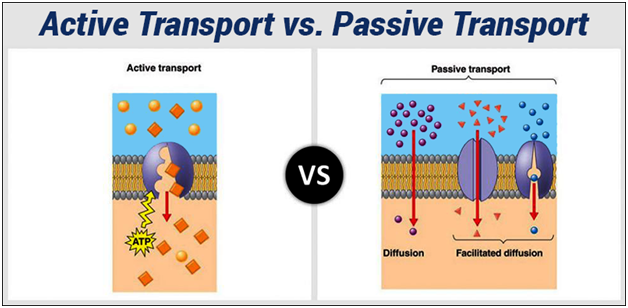
Passive transport is the moving of biochemicals across membranes of cells without the use of chemical energy. Passive diffusion of one solute across a membrane When ΔG is positive the transport is active, an input of energy is needed to move a molecule up a concentration gradient, contrary to ΔG being negative the transport is passive, which means that such molecules will pass through a membrane down their own gradient, simple diffusion. ΔV: Potential in volts across the membrane. Ζ: Electrical charge of the transported species.į: Faraday’s constant 96.5 kJ V −1 mol −1.
Taking the sum of the electrical terms and the concentration, electrical potential, generates the general expression. R: The gas constant, 8.314 x 10 −3 kJ mol −1 K −1Īt 25° (298K), ΔG is +11.4 kJ mol −1 (+2.7 kcal mol −1), indicating that this transport process requires an input of energy.įor charged species, an electrical potential is generated by an unequal distribution of ion charges across the membrane because “like” charges will be repelled.
#PASSIVE MEMBRANE TRANSPORT PROCESSES INCLUDE FREE#
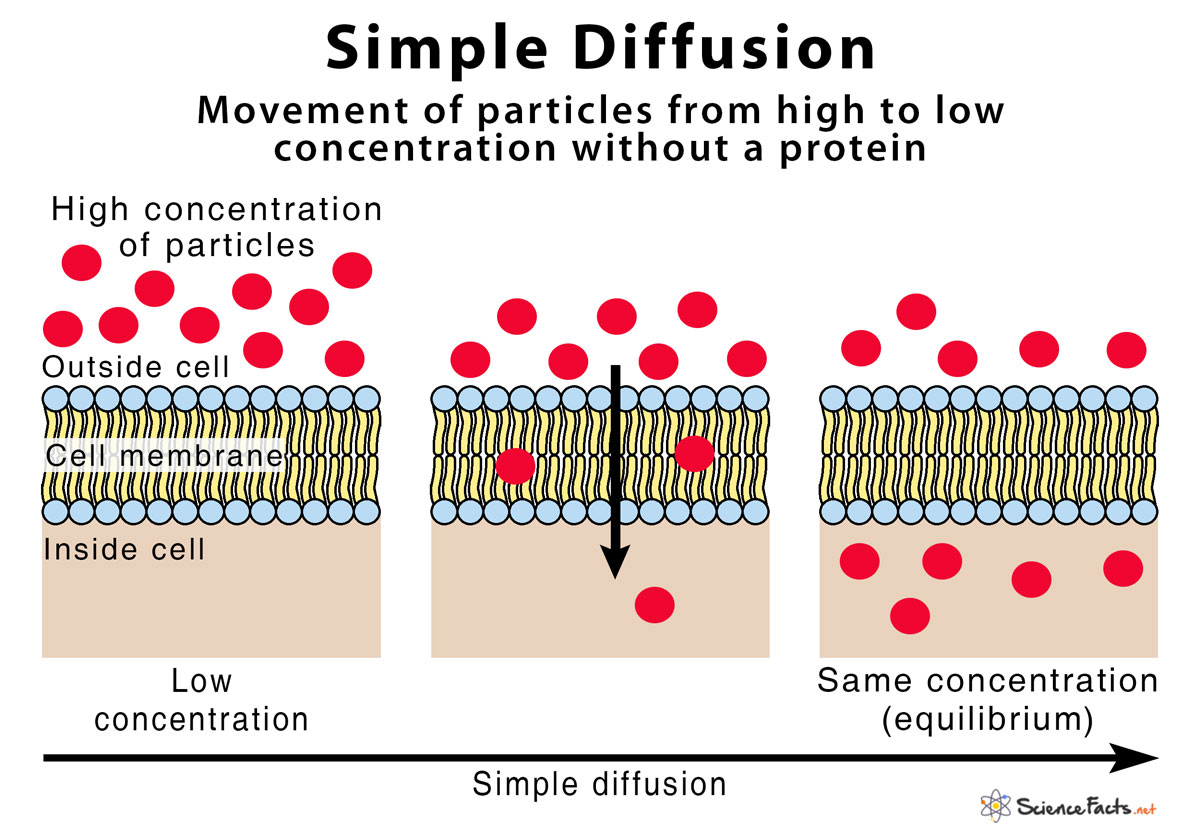
The free energy change in the transportation of an uncharged species from one side of a membrane containing a concentration of x1, to another side of a membrane containing a concentration of x2 is given as followed: The availability of free energy is one of the factors that determine if a molecule will move across a membrane, the other being the permeability of the molecule in the lipid bilayer. From the second law of thermodynamics molecules spontaneously move from a higher concentration to lower concentration. Understanding free energy is the heart of understanding how molecules are transported and/or behave in a concentration gradient. The process or movement of any molecule or ion moving down or up a concentration gradient requires a change in free energy. Quantifying Free Energy Stored In Concentration Gradients

The lipid bilayer of cell membranes is impermeable to large and polar molecules but permeable to water molecules and other small uncharged molecules like O 2 and CO 2. Examples of substances that exchange through the membrane include glucose, Na 2+, and Ca 2+, ATP, mRNA, etc. There exists an exchange of molecules and ions in and out of the cell wall, as well as in and out of membrane-bounded intracellular compartments such as the nucleus, ER, and mitrochondria. All cells need to acquire the molecules and ions that they need from their surrounding extracellular fluid.
Textbook content produced by OpenStax is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License. We recommend using aĪuthors: Mary Ann Clark, Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi Use the information below to generate a citation. Then you must include on every digital page view the following attribution: If you are redistributing all or part of this book in a digital format,
Then you must include on every physical page the following attribution: If you are redistributing all or part of this book in a print format, Want to cite, share, or modify this book? This book uses the


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
